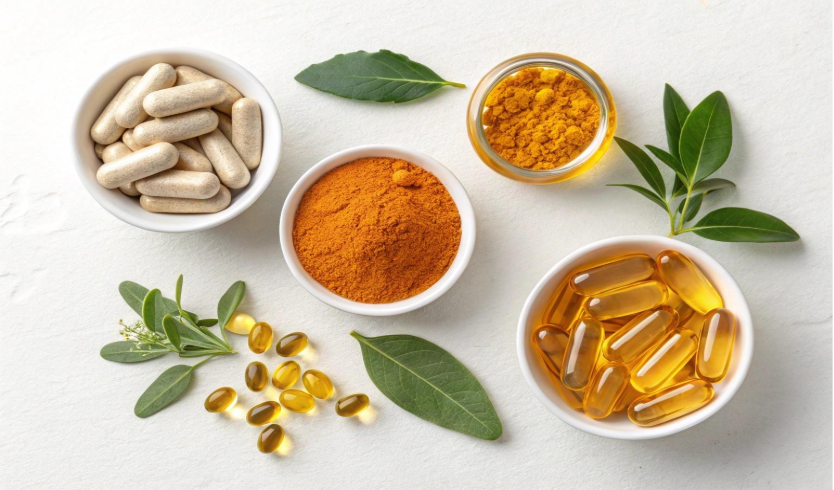
In today’s health-conscious world, supplements have become a staple in many people’s daily routines. Whether it’s vitamins, protein powders, herbal extracts, or performance boosters, the goal is often the same—improve health, support fitness, and fill nutritional gaps.
But a growing debate surrounds one fundamental question: natural vs synthetic supplements— which is safer?
Both have a place in the wellness world, but knowing the difference, benefits, and risks can make all the difference. This guide breaks down the science, sourcing, and safety behind both types so you can make informed decisions.
What Are Natural and Synthetic Supplements?
Before diving into comparisons, here’s what each term means:
- Natural Supplements:
Made from whole food sources, herbs, or natural ingredients.
Examples: Turmeric capsules, fish oil from wild fish, vitamin C from acerola cherries.
- Synthetic Supplements:
Created in labs through chemical processes to mimic natural compounds.
Examples: Lab-made vitamin D, iron tablets, synthetic vitamin E.
️ Note: Though they provide the same nutrients, how your body absorbs them can vary significantly.
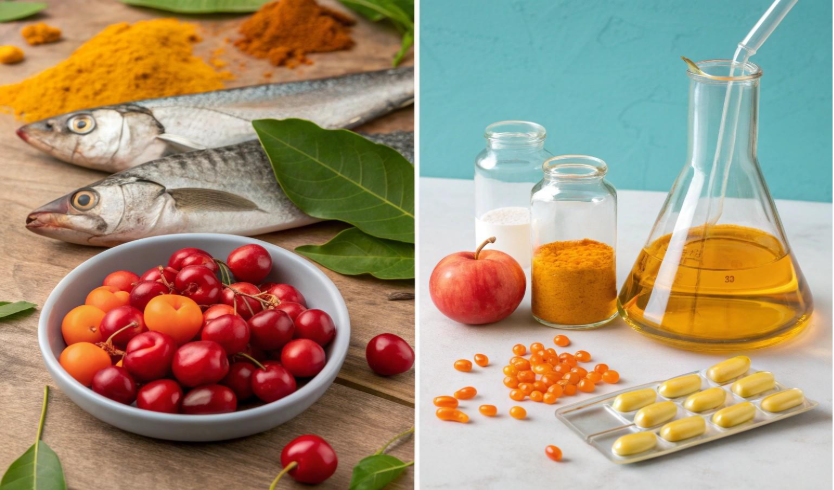

Natural Supplements: Advantages and Disadvantages

Advantages
- Better Bioavailability:
Includes co-factors that help in better absorption (e.g., Vitamin C with flavonoids).
- Fewer Additives:
Often free from artificial colors, preservatives, or fillers.
- Lower Risk of Side Effects:
As they’re closer to what the body naturally consumes.
- Eco-Friendly:
Sustainably sourced and better for the environment.
Disadvantages
- Shorter Shelf Life:
Fewer preservatives mean faster expiration.
- Unpredictable Potency:
Nutrient content may vary due to soil, harvest time, etc.
- Higher Cost:
Organic and wild-sourced ingredients are pricier.
Synthetic Supplements: Advantages and Drawbacks
Advantages
- Standardized Dosage:
Each tablet or scoop has a consistent amount.
- Longer Shelf Life:
Preservatives help retain potency longer.
- Budget-Friendly:
Cheaper to produce and buy.
- Widely Available:
Easy to find in stores and online.
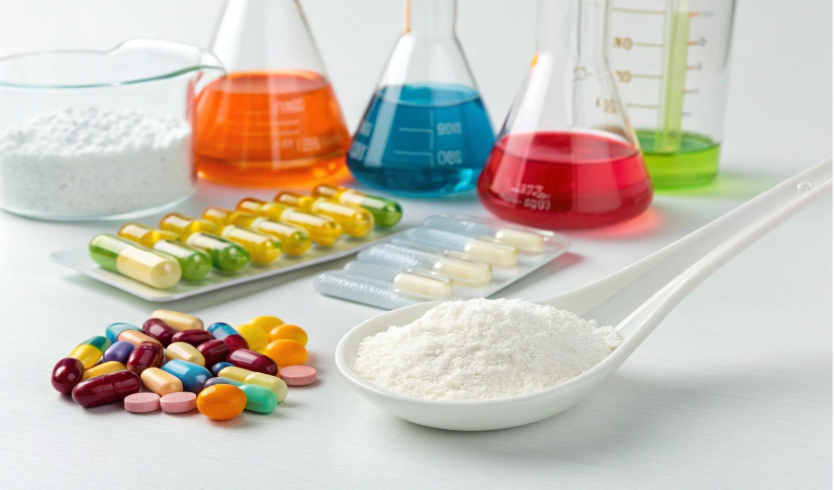

Disadvantages
- Lower Bioavailability:
The body may not absorb synthetic nutrients as well.
- Higher Risk of Reactions:
Due to added dyes, chemicals, or binders.
- Toxicity Risk:
Easy to overdose on concentrated forms (especially A, D, E, K).
- Artificial Additives:
May irritate sensitive individuals.
The Role of Organic Supplements
Organic supplements are often seen as the middle ground—combining natural sources with certified clean standards.
Benefits:
- Free of Pesticides and GMOs
- Minimal to No Additives
- Clean and Safe Option for Sensitive Users
Popular Organic Supplements:
- Plant-based protein powders
- Turmeric/Curcumin capsules
- Spirulina or chlorella
- Herbal teas and adaptogen blends

Tip: Look for third-party certification like USDA Organic to ensure purity and sustainability.
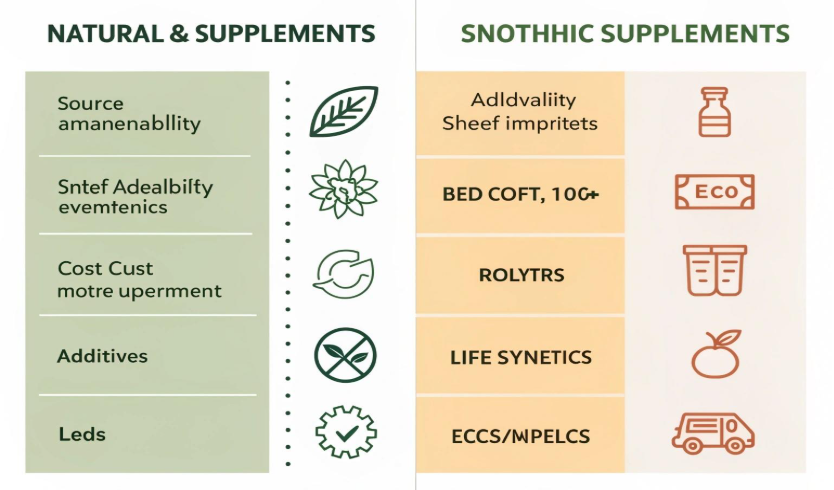
Natural vs Synthetic Supplements: Key Differences
| Feature | Natural Supplements | Synthetic Supplements |
| Source | Whole foods or herbs | Chemically manufactured |
| Bioavailability | Usually higher | May vary |
| Additives | Minimal | Often present |
| Shelf Life | Shorter | Longer |
| Cost | Higher | More affordable |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly | Higher carbon footprint |
| Side Effect Risk | Lower | Higher if misused |
Common Side Effects to Watch For
Regardless of type, side effects are possible—especially if taken incorrectly.
Potential Issues:
- Digestive problems: Bloating, gas, or constipation
- Allergic reactions: Rashes or itching (common with synthetic blends)
- Vitamin toxicity: Mostly with fat-soluble vitamins
- Drug interactions: Some ingredients can affect medications
️ Safety Tips:
- Stick to the recommended dosage
- Talk to a doctor if on medication
- Choose trusted brands with lab testing
Which One Should You Choose?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer.
Ask Yourself:
- What are your goals? Deficiency treatment or general wellness?
- Do you have allergies? Sensitive people may prefer organic.
- What’s your budget? Synthetic may be cheaper but not always better.
- How does your body respond? Track how you feel with each type.
Pro Tips for Smarter Supplement Use
Start with food:
Let real food be your primary nutrient source.
Read labels carefully:
Avoid vague ingredients or “proprietary blends.”

Look for certifications:
USDA Organic, GMP-certified, or Informed-Sport for safety.
Cycle your supplements:
Take breaks to avoid dependence or reduced effectiveness.
Listen to your body:
If something feels off, stop and consult a healthcare provider.
Final Verdict: What’s Safer?
Both natural and synthetic supplements come with their own set of pros and cons.
Synthetic supplements may be more accessible and affordable.
- Natural and organic supplements are generally cleaner, safer, and better absorbed.The best supplement is the one that fits your goals, budget, and body.
Conclusion: Make an Informed Choice
Your body deserves more than guesswork.
Choose supplements with intention, transparency, and quality.
When in doubt, always prioritize whole foods, ask for expert advice, and listen to how your body responds.




